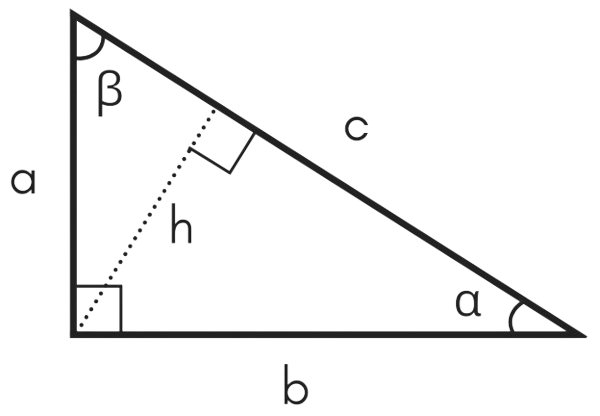
Right Triangle Calculator
The Right Triangle Calculator helps calculate any unknown value in a right-angled triangle—be it the perpendicular (a), base (B), hypotenuse (C), area (A), perimeter (P), angle α (Alpha), angle β (Beta), or altitude (H). By simply providing any two known values, the calculator quickly adapts to your input and delivers accurate results along with step-by-step solutions.
This calculator uses right triangle formulas to find the side a, side b, hypotenuse (c), area (A), perimeter (P), altitude (h), and angles α and β, depending on what values you enter. It’s designed for students, teachers, engineers, and anyone needing fast and accurate right triangle calculations.
Accepted Input Combinations
You can use a wide variety of input pairs to calculate the missing values in a right triangle. Below are the supported input combinations and what the calculator can solve for:
1. Two Sides Given
- a & b (Legs)
- a & c (Leg & Hypotenuse)
- b & c (Leg & Hypotenuse)
2. Area and One Side
- Area & a
- Area & b
- Area & c
3. Angle and One Side
- a & ∠α
- a & ∠β
- b & ∠α
- b & ∠β
- c & ∠α
- c & ∠β
4. Perimeter and One Side
- Perimeter & a
- Perimeter & b
- Perimeter & c
5. Perimeter and Area
- Perimeter & Area
6. Altitude and One Side
- a & Altitude (h)
- b & Altitude (h)
- c & Altitude (h)
7. Altitude and Area or Perimeter
- Area & Altitude (h)
- Perimeter & Altitude (h)
Outputs Provided by the Calculator
Based on your selected input, the Area of a Right Triangle Calculator will compute and display:
- Side a (Perpendicular)
- Side b (Base)
- Hypotenuse (c)
- Area (A)
- Perimeter (P)
- Altitude (h)
- Angle α (opposite side a)
- Angle β (opposite side b)
Note: The Right Triangle Calculator helps to calculate any unknown value in a right-angled triangle—be it the perpendicular (a), base (B), hypotenuse (C), area (A), perimeter (P), angle α (Alpha), angle β (Beta), or altitude (H). By simply providing any two known values, the calculator intelligently applies geometric and trigonometric formulas to solve for the rest. It supports multiple units for length—meters (m), centimeters (cm), millimeters (mm), yards (yd), feet (ft), and inches (in)—as well as angle units in both degrees and radians.
How to Use the Right Triangle Calculator
1. Select Your Input Type: Use the dropdown menu labeled “Given” to choose one of the following options:
- a & b (Legs)
- a & c (Leg & Hypotenuse)
- b & c (Leg & Hypotenuse)
- Area & a
- Area & b
- Area & c
- a & ∠α
- a & ∠β
- b & ∠α
- b & ∠β
- c & ∠α
- c & ∠β
- Perimeter & a
- Perimeter & b
- Perimeter & c
- Perimeter & Area
- a & Altitude (h)
- b & Altitude (h)
- c & Altitude (h)
- Area & Altitude (h)
- Perimeter & Altitude (h)
2. Enter Known Values: In this calculator, you can calculate key properties of a right triangle such as the perpendicular (a), base (b), hypotenuse (c), area, perimeter, angle α, angle β, and altitude (h). The calculator works by allowing you to enter any two known values, and it will automatically compute the remaining quantities with accurate results.
3. Choose Decimal Precision:
- Select how many decimal places you want the result to be rounded to (e.g., 3)
- Select Units:
- Length Units: Meters (m), Centimeters (cm), Millimeters (mm), Yards (yd), Feet (ft), Inches (in)
- Angle Units: Degrees (°), Radians (rad)
4. Click “Calculate”: The calculator will compute the all unknown.
5. Hide Steps: Toggle this option to hide or show detailed calculation steps.
6. Reset: Clear all inputs to start a new calculation.
Right Triangle Calculator
Important Formulas Used in This Right Triangle Calculator
The Right Triangle Calculator uses a variety of geometric and trigonometric formulas to calculate all the missing values of a right triangle based on the two inputs you provide. Below are the key formulas this calculator applies:
Area of a Right Triangle
$A = \frac{1}{2} \times a \times b$
This formula calculates the area of a right-angled triangle where $a$ and $b$ are the two perpendicular sides (base and height).
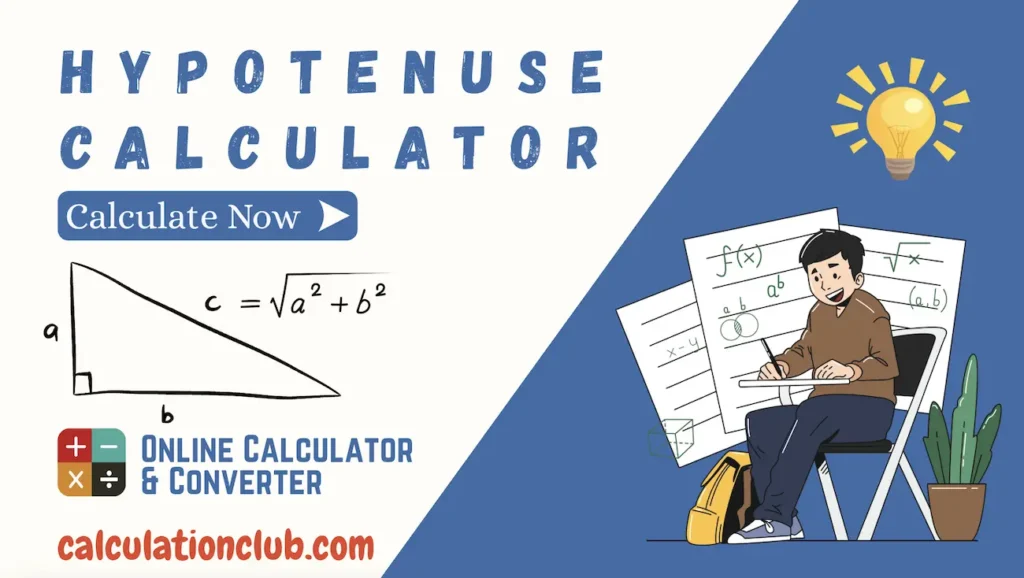
Pythagorean Theorem
$c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2}$
This determines the hypotenuse $c$ in a right triangle when the two legs $a$ and $b$ are known.
Perimeter of Triangle
$P = a + b + c$
The perimeter is the sum of all three sides of the triangle: $a$, $b$, and hypotenuse $c$.
Altitude from Hypotenuse
$h = \frac{a \times b}{c}$
This formula gives the height ($h$) dropped from the right angle to the hypotenuse $c$, based on the two perpendicular sides $a$ and $b$.
Angle $\alpha$ (opposite side $a$)
$\alpha = \arcsin\left(\frac{a}{c}\right)$ or $\alpha = \arctan\left(\frac{a}{b}\right)$
These equations calculate angle $\alpha$ using either sine or tangent, depending on which sides are known.
Angle $\beta$ (opposite side $b$)
$\beta = 90^\circ – \alpha$
Since the triangle is right-angled, the two other angles must add up to $90^\circ$. Subtracting $\alpha$ gives angle $\beta$.
Side $a$ (from Area and $b$)
$a = \frac{2A}{b}$
If the area $A$ and one side $b$ are known, this formula solves for side $a$.
Side $b$ (from Area and $a$)
$b = \frac{2A}{a}$
This calculates side $b$ when the area and side $a$ are given.
Derivation of the Formula
\( c = \sqrt{ \frac{a^2}{1 – \frac{h^2}{a^2}} } \)
Step 1: Use the formula for the altitude from the right angle to the hypotenuse:
\( h = \frac{a \cdot b}{c} \)
Step 2: Use the Pythagorean theorem to express \( b \) in terms of \( c \) and \( a \):
\( b^2 = c^2 – a^2 \Rightarrow b = \sqrt{c^2 – a^2} \)
Step 3: Substitute this into the altitude formula:
\( h = \frac{a \cdot \sqrt{c^2 – a^2}}{c} \)
Step 4: Square both sides to eliminate the square root:
$ h^2 $$= \left( \frac{a \cdot \sqrt{c^2 – a^2}}{c} \right)^2 $$= \frac{a^2 (c^2 – a^2)}{c^2} $
Step 5: Multiply both sides by \( c^2 \):
\( h^2 c^2 = a^2(c^2 – a^2) \)
Step 6: Expand and rearrange:
\( h^2 c^2 = a^2 c^2 – a^4 \)
$ h^2 c^2 – a^2 c^2 = -a^4 $
$\Rightarrow c^2(h^2 – a^2) = -a^4$
Multiply both sides by -1:
\( c^2(a^2 – h^2) = a^4 \)
Step 7: Solve for \( c \):
\( c^2 = \frac{a^4}{a^2 – h^2} \Rightarrow c = \sqrt{ \frac{a^4}{a^2 – h^2} } \)
Now simplify:
\( c = \sqrt{ \frac{a^2}{1 – \frac{h^2}{a^2}} } \)
Final Formula:
$ \boxed{c = \sqrt{ \frac{a^2}{1 – \frac{h^2}{a^2}} } } $
Similer:
$ \boxed{c = \sqrt{ \frac{b^2}{1 – \frac{h^2}{b^2}} } } $
Derivation of the Formula
\( c = \frac{P^2}{2(P + h)} \)
Let the sides of a right triangle be:
- \( a \), \( b \): the legs
- \( c \): the hypotenuse
- \( h \): the altitude to hypotenuse
- \( P \): the perimeter, \( P = a + b + c \)
Step 1: Express sum of legs
From the perimeter formula:
$a + b = P – c \tag{1}$
Step 2: Use area identity involving altitude
The altitude to the hypotenuse is given by:
$h = \frac{ab}{c} \Rightarrow ab = ch \tag{2}$
Step 3: Use identity for squared sum
$(a + b)^2 = a^2 + b^2 + 2ab$
From Pythagoras: \( a^2 + b^2 = c^2 \)
So:
$(a + b)^2 = c^2 + 2ab \tag{3}$
Step 4: Substitute known expressions
From (1): \( a + b = P – c \)
From (2): \( ab = ch \)
So substitute into (3):
$(P – c)^2$$ = c^2 + 2ch$
Step 5: Expand and simplify
$P^2 – 2Pc + c^2 $$= c^2 + 2ch$
Subtract \( c^2 \) from both sides:
$P^2 – 2Pc = 2ch$
Step 6: Solve for \( c \)
$P^2 = 2c(P + h)$
$\Rightarrow \boxed{c = \frac{P^2}{2(P + h)}}$
Right Triangle Calculator Example.1 : Find All Remaining Parts of a Right Triangle Given \(a = 3\) and \(b = 4\)
Given:
\( a = 3 \) units (one leg)
\( b = 4 \) units (other leg)
Find: hypotenuse \( c \), area \( A \), perimeter \( P \), altitude \( h \), angles \( \alpha \) and \( \beta \)
Step 1: Find the hypotenuse \( c \) using Pythagorean theorem
$c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} $$= \sqrt{3^2 + 4^2} $$= \sqrt{9 + 16} $$= \sqrt{25} = 5$
Step 2: Find the area \( A \)
$A = \frac{1}{2} \times a \times b $$= \frac{1}{2} \times 3 \times 4 = 6$
Step 3: Find the perimeter \( P \)
$P = a + b + c $$= 3 + 4 + 5 = 12$
Step 4: Find the altitude \( h \) from the right angle to hypotenuse
$h = \frac{a \times b}{c} $$= \frac{3 \times 4}{5} $$= \frac{12}{5} = 2.4$
Step 5: Find angle \( \alpha \) (opposite side \( b \)) using tan⁻¹
$\alpha = \tan^{-1}\left(\frac{b}{a}\right) $$= \tan^{-1}\left(\frac{4}{3}\right) \approx 53.13^\circ$
Step 6: Find angle \( \beta \) (opposite side \( a \))
$\beta = 90^\circ – \alpha $$= 90^\circ – 53.13^\circ $$= 36.87^\circ$
Right Triangle Calculator Example.2 : Find All Remaining Parts of a Right Triangle Given \(a = 3\) and \(c = 5\)
Given:
\( a = 3 \) units (one leg)
\( c = 5 \) units (hypotenuse)
Find:
other leg \( b \), area \( A \), perimeter \( P \), altitude \( h \), angles \( \alpha \) and \( \beta \)
Step 1: Find the other leg \( b \) using Pythagorean theorem
$b = \sqrt{c^2 – a^2} $$= \sqrt{5^2 – 3^2} $$= \sqrt{25 – 9} $$= \sqrt{16} = 4$
Step 2: Find the area \( A \)
$A = \frac{1}{2} \times a \times b $$= \frac{1}{2} \times 3 \times 4 $$= 6$
Step 3: Find the perimeter \( P \)
$P = a + b + c $$= 3 + 4 + 5 = 12$
Step 4: Find the altitude \( h \) from the right angle to hypotenuse
$h = \frac{a \times b}{c} $$= \frac{3 \times 4}{5} $$= \frac{12}{5} = 2.4$
Step 5: Find angle \( \alpha \) (opposite side \( b \)) using \(\tan^{-1}\)
$\alpha = \tan^{-1}\left(\frac{b}{a}\right) $$= \tan^{-1}\left(\frac{4}{3}\right) \approx 53.13^\circ$
Step 6: Find angle \( \beta \) (opposite side \( a \))
$\beta = 90^\circ – \alpha $$= 90^\circ – 53.13^\circ $$= 36.87^\circ$
Right Triangle Calculator Example.3 : Find All Remaining Parts of a Right Triangle Given \(b = 4\) and \(c = 5\)
Given:
\( b = 4 \) units (one leg)
\( c = 5 \) units (hypotenuse)
Find:
other leg \( a \), area \( A \), perimeter \( P \), altitude \( h \), angles \( \alpha \) and \( \beta \)
Step 1: Find the other leg \( a \) using Pythagorean theorem
$a = \sqrt{c^2 – b^2} $$= \sqrt{5^2 – 4^2} $$= \sqrt{25 – 16} $$= \sqrt{9} = 3$
Step 2: Find the area \( A \)
$A = \frac{1}{2} \times a \times b $$= \frac{1}{2} \times 3 \times 4 = 6$
Step 3: Find the perimeter \( P \)
$P = a + b + c $$= 3 + 4 + 5 = 12$
Step 4: Find the altitude \( h \) from the right angle to hypotenuse
$h = \frac{a \times b}{c} $$= \frac{3 \times 4}{5} $$= \frac{12}{5} = 2.4$
Step 5: Find angle \( \alpha \) (opposite side \( b \)) using \(\tan^{-1}\)
$\alpha = \tan^{-1}\left(\frac{b}{a}\right) $$= \tan^{-1}\left(\frac{4}{3}\right) \approx 53.13^\circ$
Step 6: Find angle \( \beta \) (opposite side \( a \))
$\beta = 90^\circ – \alpha$$ = 90^\circ – 53.13^\circ$$ = 36.87^\circ$
Right Triangle Calculator Example.4 : Find All Remaining Parts of a Right Triangle Given Area \( A = 6 \) and side \( a = 3 \)
Given:
\( A = 6 \) square units (area)
\( a = 3 \) units (one leg)
Find:
other leg \( b \), hypotenuse \( c \), perimeter \( P \), altitude \( h \), angles \( \alpha \) and \( \beta \)
Step 1: Find leg \( b \) using area formula
$A = \frac{1}{2} \times a \times b \Rightarrow b = \frac{2A}{a} = \frac{2 \times 6}{3} = \frac{12}{3} = 4$
Step 2: Find the hypotenuse \( c \)
$c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} = \sqrt{3^2 + 4^2} = \sqrt{9 + 16} = \sqrt{25} = 5$
Step 3: Find the perimeter \( P \)
$P = a + b + c = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12$
Step 4: Find the altitude \( h \)
$h = \frac{a \times b}{c} = \frac{3 \times 4}{5} = \frac{12}{5} = 2.4$
Step 5: Find angle \( \alpha \) (opposite side \( b \))
$\alpha = \tan^{-1}\left(\frac{b}{a}\right) = \tan^{-1}\left(\frac{4}{3}\right) \approx 53.13^\circ$
Step 6: Find angle \( \beta \) (opposite side \( a \))
$\beta = 90^\circ – \alpha = 36.87^\circ$
Right Triangle Calculator Example.5 : Find All Remaining Parts of a Right Triangle Given Area \( A = 6 \) and side \( b = 4 \)
Given:
\( A = 6 \) square units (area)
\( b = 4 \) units (one leg)
Find:
other leg \( a \), hypotenuse \( c \), perimeter \( P \), altitude \( h \), angles \( \alpha \) and \( \beta \)
Step 1: Find leg \( a \) using area formula
$A = \frac{1}{2} \times a \times b \Rightarrow a $$= \frac{2A}{b} = \frac{2 \times 6}{4} $$= \frac{12}{4} = 3$
Step 2: Find the hypotenuse \( c \)
$c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} $$= \sqrt{3^2 + 4^2} $$= \sqrt{9 + 16} $$= \sqrt{25} = 5$
Step 3: Find the perimeter \( P \)
$P = a + b + c $$= 3 + 4 + 5 = 12$
Step 4: Find the altitude \( h \)
$h = \frac{a \times b}{c} $$= \frac{3 \times 4}{5} $$= \frac{12}{5} = 2.4$
Step 5: Find angle \( \alpha \) (opposite side \( b \))
$\alpha = \tan^{-1}\left(\frac{b}{a}\right) $$= \tan^{-1}\left(\frac{4}{3}\right) \approx 53.13^\circ$
Step 6: Find angle \( \beta \) (opposite side \( a \))
$\beta = 90^\circ – \alpha $$= 36.87^\circ$
Right Triangle Calculator Example.6 : Find All Remaining Parts of a Right Triangle Given Area \( A = 6 \) and hypotenuse \( c = 5 \)
Given:
\( A = 6 \) square units (area)
\( c = 5 \) units (hypotenuse)
Find:
legs \( a \) and \( b \), perimeter \( P \), altitude \( h \), angles \( \alpha \) and \( \beta \)
Step 1: Use identity \( A = \frac{a \times b}{2} \) and \( a^2 + b^2 = c^2 \)
We solve:
$a \times b $$= 12 \quad \text{(from area)}$
$a^2 + b^2 $$= 25 \quad \text{(from Pythagoras)}$
Solving these equations gives \( a = 3 \), \( b = 4 \)
Step 2: Find the perimeter \( P \)
$P = a + b + c $$= 3 + 4 + 5 = 12$
Step 3: Find the altitude \( h \)
$h = \frac{a \times b}{c} $$= \frac{3 \times 4}{5} = 2.4$
Step 4: Find angle \( \alpha \) (opposite side \( b \))
$\alpha$$ = \tan^{-1}\left(\frac{b}{a}\right) $$= \tan^{-1}\left(\frac{4}{3}\right) \approx 53.13^\circ$
Step 5: Find angle \( \beta \) (opposite side \( a \))
$\beta = 90^\circ – \alpha $$= 36.87^\circ$
Right Triangle Calculator Example.7 : Find All Remaining Parts of a Right Triangle Given side \( a = 3 \) and angle \( \alpha = 36.87^\circ \)
Given:
\( a = 3 \) units (one leg)
\( \alpha = 36.87^\circ \) (angle opposite side \( a \))
Find:
other leg \( b \), hypotenuse \( c \), area \( A \), perimeter \( P \), altitude \( h \), angle \( \beta \)
Step 1: Find angle \( \beta \)
$\beta = 90^\circ – \alpha $$= 90^\circ – 36.87^\circ $$= 53.13^\circ$
Step 2: Find side \( b \) using tangent
$\tan(\beta) = \frac{b}{a} \Rightarrow b $$= a \cdot \tan(\beta) $$= 3 \cdot \tan(53.13^\circ) \approx 3 \cdot 1.333 = 4$
Step 3: Find hypotenuse \( c \)
$c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} $$= \sqrt{3^2 + 4^2} $$= \sqrt{25} = 5$
Step 4: Find area \( A \)
$A = \frac{1}{2} \cdot a \cdot b $$= \frac{1}{2} \cdot 3 \cdot 4 = 6$
Step 5: Find perimeter \( P \)
$P = a + b + c $$= 3 + 4 + 5 $$= 12$
Step 6: Find altitude \( h \)
$h = \frac{a \cdot b}{c} $$= \frac{12}{5} = 2.4$
Right Triangle Calculator Example.8 : Find All Remaining Parts of a Right Triangle Given side \( a = 3 \) and angle \( \beta = 53.13^\circ \)
Given:
\( a = 3 \) units (adjacent to angle \( \beta \))
\( \beta = 53.13^\circ \)
Find:
other leg \( b \), hypotenuse \( c \), area \( A \), perimeter \( P \), altitude \( h \), angle \( \alpha \)
Step 1: Find angle \( \alpha \)
$\alpha = 90^\circ – \beta $$= 90^\circ – 53.13^\circ $$= 36.87^\circ$
Step 2: Find side \( b \)
$\tan(\beta) = \frac{b}{a} \Rightarrow b $$= a \cdot \tan(53.13^\circ) $$= 3 \cdot 1.333 = 4$
Step 3: Find hypotenuse \( c \)
$c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} $$= \sqrt{9 + 16} = 5$
Step 4: Find area \( A \)
$A = \frac{1}{2} \cdot a \cdot b = 6$
Step 5: Find perimeter \( P \)
$P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12$
Step 6: Find altitude \( h \)
$h = \frac{3 \cdot 4}{5} = 2.4$
Right Triangle Calculator Example.9 : Find All Remaining Parts of a Right Triangle Given side \( b = 4 \) and angle \( \alpha = 36.87^\circ \)
Given:
\( b = 4 \) units (opposite angle \( \alpha \))
\( \alpha = 36.87^\circ \)
Find:
side \( a \), hypotenuse \( c \), area \( A \), perimeter \( P \), altitude \( h \), angle \( \beta \)
Step 1: Find angle \( \beta \)
$\beta = 90^\circ – \alpha $$= 53.13^\circ$
Step 2: Find side \( a \)
$\tan(\alpha) = \frac{b}{a} \Rightarrow a $$= \frac{b}{\tan(\alpha)} $$= \frac{4}{0.75} = 3$
Step 3: Find hypotenuse \( c \)
$c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} $$= 5$
Step 4: Find area \( A \)
$A = \frac{1}{2} \cdot a \cdot b $$= 6$
Step 5: Find perimeter \( P \)
$P = 3 + 4 + 5 $$= 12$
Step 6: Find altitude \( h \)
$h = 2.4$
Right Triangle Calculator Example.10 : Find All Remaining Parts of a Right Triangle Given side \( b = 4 \) and angle \( \beta = 53.13^\circ \)
Given:
\( b = 4 \) units
\( \beta = 53.13^\circ \)
Find:
side \( a \), hypotenuse \( c \), area \( A \), perimeter \( P \), altitude \( h \), angle \( \alpha \)
Step 1: Find angle \( \alpha \)
$\alpha = 90^\circ – \beta $$= 36.87^\circ$
Step 2: Find side \( a \)
$\tan(\alpha) = \frac{b}{a} \Rightarrow a $$= \frac{b}{\tan(\alpha)} $$= \frac{4}{0.75} = 3$
Step 3: Find hypotenuse \( c \)
$c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2}$$ = 5$
Step 4: Find area \( A \)
$A = \frac{1}{2} \cdot 3 \cdot 4 $$= 6$
Step 5: Find perimeter \( P \)
$P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12$
Step 6: Find altitude \( h \)
$h = 2.4$
Right Triangle Calculator Example.11 : Find All Remaining Parts of a Right Triangle Given hypotenuse \( c = 5 \) and angle \( \alpha = 36.87^\circ \)
Given:
\( c = 5 \) units
\( \alpha = 36.87^\circ \)
Find:
sides \( a \), \( b \), area \( A \), perimeter \( P \), altitude \( h \), angle \( \beta \)
Step 1: Find angle \( \beta \)
$\beta = 90^\circ – \alpha $$= 53.13^\circ$
Step 2: Use sine to find \( a \)
$\sin(\alpha) = \frac{a}{c} \Rightarrow a $$= c \cdot \sin(\alpha) $$= 5 \cdot 0.6 = 3$
Step 3: Use cosine to find \( b \)
$\cos(\alpha) = \frac{b}{c} \Rightarrow b $$= 5 \cdot 0.8 = 4$
Step 4: Find area \( A \)
$A = \frac{1}{2} \cdot 3 \cdot 4 $$= 6$
Step 5: Find perimeter \( P \)
$P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12$
Step 6: Find altitude \( h \)
$h = \frac{3 \cdot 4}{5} = 2.4$
Right Triangle Calculator Example.12 : Find All Remaining Parts of a Right Triangle Given hypotenuse \( c = 5 \) and angle \( \beta = 53.13^\circ \)
Given:
\( c = 5 \) units
\( \beta = 53.13^\circ \)
Find:
sides \( a \), \( b \), area \( A \), perimeter \( P \), altitude \( h \), angle \( \alpha \)
Step 1: Find angle \( \alpha \)
$\alpha = 90^\circ – \beta = 36.87^\circ$
Step 2: Use sine to find \( b \)
$\sin(\beta) = \frac{b}{c} \Rightarrow b $$= 5 \cdot \sin(53.13^\circ) = 5 \cdot 0.8 = 4$
Step 3: Use cosine to find \( a \)
$\cos(\beta) = \frac{a}{c} \Rightarrow a $$= 5 \cdot 0.6 = 3$
Step 4: Find area \( A \)
$A = \frac{1}{2} \cdot 3 \cdot 4 $$= 6$
Step 5: Find perimeter \( P \)
$P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12$
Step 6: Find altitude \( h \)
$h = \frac{3 \cdot 4}{5} = 2.4$
Right Triangle Calculator Example.13 : Find All Remaining Parts of a Right Triangle Given Perimeter \( P = 12 \) and side \( a = 3 \)
Given:
\( P = 12 \) units (perimeter)
\( a = 3 \) units (one leg)
Find:
other leg \( b \), hypotenuse \( c \), area \( A \), altitude \( h \), angles \( \alpha \) and \( \beta \)
Step 1: Use identity \( a + b + c = P \) and \( a^2 + b^2 = c^2 \)
Solve system:
- \( a + b + \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} = 12 \)
- Substitute \( a = 3 \), solve numerically to get \( b = 4 \), \( c = 5 \)
Step 2: Find area \( A \)
$ A = \frac{1}{2} \times a \times b $$= \frac{1}{2} \times 3 \times 4 = 6 $ square units
Step 3: Find altitude \( h \)
$ h = \frac{a \times b}{c} $$= \frac{3 \times 4}{5} = 2.4 $units
Step 4: Find angles
$\alpha = \tan^{-1}\left(\frac{b}{a}\right) $$= \tan^{-1}\left(\frac{4}{3}\right) \approx 53.13^\circ $
\( \beta = 90^\circ – \alpha = 36.87^\circ \)
Right Triangle Calculator Example.14 : Find All Remaining Parts of a Right Triangle Given Perimeter \( P = 12 \) and side \( b = 4 \)
Given:
\( P = 12 \) units (perimeter)
\( b = 4 \) units (one leg)
Find:
other leg \( a \), hypotenuse \( c \), area \( A \), altitude \( h \), angles \( \alpha \) and \( \beta \)
Step 1: Use system \( b + a + \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} = 12 \)
Substitute \( b = 4 \), solve:
- \( a + 4 + \sqrt{a^2 + 16} = 12 \)
- Numerically solving gives \( a = 3 \), \( c = 5 \)
Step 2: Find area \( A \)
$ A = \frac{1}{2} \times a \times b $$= \frac{1}{2} \times 3 \times 4 = 6 $square units
Step 3: Find altitude \( h \)
\( h = \frac{3 \times 4}{5} = 2.4 \) units
Step 4: Find angles
$ \alpha = \tan^{-1}\left(\frac{b}{a}\right) \approx 53.13^\circ$
$ \beta = 90^\circ – \alpha = 36.87^\circ$
Right Triangle Calculator Example.15 : Find All Remaining Parts of a Right Triangle Given Perimeter \( P = 12 \) and hypotenuse \( c = 5 \)
Given:
\( P = 12 \) units (perimeter)
\( c = 5 \) units (hypotenuse)
Find:
legs \( a \) and \( b \), area \( A \), altitude \( h \), angles \( \alpha \) and \( \beta \)
Step 1: Use system \( a + b + 5 = 12 \Rightarrow a + b = 7 \) and \( a^2 + b^2 = 25 \)
Solve:
- Substitute \( b = 7 – a \) into Pythagoras
- Solve: \( a^2 + (7 – a)^2 = 25 \Rightarrow a = 3 \), \( b = 4 \)
Step 2: Area
$ A = \frac{1}{2} \times a \times b$$ = \frac{1}{2} \times 3 \times 4 = 6$
Step 3: Altitude
$ h = \frac{3 \times 4}{5} = 2.4$
Step 4: Angles
$\alpha = \tan^{-1}\left(\frac{4}{3}\right) \approx 53.13^\circ $
$\beta = 90^\circ – \alpha = 36.87^\circ$
Right Triangle Calculator Example.16 : Find All Remaining Parts of a Right Triangle Given Perimeter \( P = 12 \) and Area \( A = 6 \)
Given:
\( P = 12 \) units (perimeter)
\( A = 6 \) square units
Find:
sides \( a \), \( b \), \( c \), altitude \( h \), angles \( \alpha \), \( \beta \)
Step 1: Use system:
- \( a + b + \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} = 12 \)
- \( \frac{1}{2} \times a \times b = 6 \Rightarrow ab = 12 \)
Solving this system gives: \( a = 3 \), \( b = 4 \), \( c = 5 \)
Step 2: Altitude
$ h = \frac{ab}{c} = \frac{12}{5} = 2.4$
Step 3: Angles
\( \alpha = \tan^{-1}\left(\frac{4}{3}\right) \approx 53.13^\circ \)
\( \beta = 90^\circ – \alpha = 36.87^\circ \)
Right Triangle Calculator Example.17 : Find All Remaining Parts of a Right Triangle Given Side \( a = 3 \) and Altitude \( h = 2.4 \)
Given:
\( a = 3 \) units (leg)
\( h = 2.4 \) units (altitude to hypotenuse)
Find:
other side \( b \), hypotenuse \( c \), area \( A \), perimeter \( P \), angles \( \alpha \), \( \beta \)
Step 1: Use formula to find hypotenuse \( c \)
$c = \sqrt{\frac{a^2}{1 – \frac{h^2}{a^2}}} $$= \sqrt{\frac{9}{1 – \frac{5.76}{9}}} $$= \sqrt{\frac{9}{1 – 0.64}} $$= \sqrt{\frac{9}{0.36}} = \sqrt{25} = 5$
Step 2: Find side \( b \) using Pythagoras
$b $$= \sqrt{c^2 – a^2} = \sqrt{25 – 9} $$= \sqrt{16} = 4$
Step 3: Find Area \( A \)
$A = \frac{1}{2} \times a \times b $$= \frac{1}{2} \times 3 \times 4 = 6$
Step 4: Find Perimeter \( P \)
$P = a + b + c = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12$
Step 5: Find Angles
$\alpha = \tan^{-1}\left(\frac{b}{a}\right) $$= \tan^{-1}\left(\frac{4}{3}\right) \approx 53.13^\circ$
$\beta = 90^\circ – \alpha = 36.87^\circ$
Right Triangle Calculator Example.18 : Find All Remaining Parts of a Right Triangle Given Side \( b = 4 \) and Altitude \( h = 2.4 \)
Given:
\( b = 4 \) units (leg)
\( h = 2.4 \) units (altitude to hypotenuse)
Find:
other side \( a \), hypotenuse \( c \), area \( A \), perimeter \( P \), angles \( \alpha \), \( \beta \)
Step 1: Use formula to find hypotenuse \( c \)
$c = \sqrt{\frac{b^2}{1 – \frac{h^2}{b^2}}} $$= \sqrt{\frac{16}{1 – \frac{5.76}{16}}} $$= \sqrt{\frac{16}{1 – 0.36}} $$= \sqrt{\frac{16}{0.64}} $$= \sqrt{25} = 5$
Step 2: Find side \( a \) using Pythagoras
$a = \sqrt{c^2 – b^2} = \sqrt{25 – 16} = \sqrt{9} = 3$
Step 3: Find Area \( A \)
$A = \frac{1}{2} \times a \times b = \frac{1}{2} \times 3 \times 4 = 6$
Step 4: Find Perimeter \( P \)
$P = a + b + c = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12$
Step 5: Find Angles
$\alpha = \tan^{-1}\left(\frac{b}{a}\right) = \tan^{-1}\left(\frac{4}{3}\right) \approx 53.13^\circ$
$\beta = 90^\circ – \alpha = 36.87^\circ$
Right Triangle Calculator Example.19 : Find All Remaining Parts of a Right Triangle Given Hypotenuse \( c = 5 \) and Altitude \( h = 2.4 \)
Given:
\( c = 5 \) units
\( h = 2.4 \) units
Find:
sides \( a \), \( b \), area \( A \), perimeter \( P \), angles \( \alpha \), \( \beta \)
Step 1: Use $ A = \frac{1}{2} \times c \times h $$= \frac{1}{2} \times 5 \times 2.4 = 6$
Then use \( ab = 12 \), and \( a^2 + b^2 = 25 \)
Solving gives \( a = 3 \), \( b = 4 \)
Step 2: Perimeter
\( P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \)
Step 3: Angles
\( \alpha = 53.13^\circ \), \( \beta = 36.87^\circ \)
Right Triangle Calculator Example.20 : Find All Remaining Parts of a Right Triangle Given Area \( A = 6 \) and Altitude \( h = 2.4 \)
Given:
\( A = 6 \) square units
\( h = 2.4 \) units
Find:
sides \( a \), \( b \), \( c \), perimeter \( P \), angles \( \alpha \), \( \beta \)
Step 1: Use \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times c \times h \)
$\Rightarrow c = \frac{2A}{h} = \frac{12}{2.4} = 5 $
Now, \( ab = 12 \), and \( a^2 + b^2 = 25 \) → solving gives \( a = 3 \), \( b = 4 \)
Step 2: Perimeter
\( P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \)
Step 3: Angles
\( \alpha = 53.13^\circ \), \( \beta = 36.87^\circ \)
Right Triangle Calculator Example.21 : Find All Remaining Parts of a Right Triangle Given Altitude \( h = 2.4 \) and Perimeter \( P = 12 \)
Given:
Altitude \( h = 2.4 \) meters (from right angle to hypotenuse)
Perimeter \( P = 12 \) meters
Find:
Sides \( a \), \( b \), hypotenuse \( c \), area \( A \), angles \( \alpha \), \( \beta \)
Step 1: Use formula to find hypotenuse \( c \)
We use the formula:
$c = \frac{P^2}{2(P + h)}$$ = \frac{12^2}{2(12 + 2.4)} $$= \frac{144}{2 \times 14.4} $$= \frac{144}{28.8} = 5 $
Step 2: Use perimeter relation to find sum of legs
Since \( P = a + b + c \), and \( c = 5 \):
\( a + b = 12 – 5 = 7 \)
Let \( a = x \), then \( b = 7 – x \)
Step 3: Use the Pythagorean Theorem
\( a^2 + b^2 = c^2 = 25 \)
Substitute \( b = 7 – x \):
\( x^2 + (7 – x)^2 = 25 \)
\( x^2 + 49 – 14x + x^2 = 25 \)
\( 2x^2 – 14x + 49 = 25 \)
\( 2x^2 – 14x + 24 = 0 \)
Solve the quadratic equation:
\( x = 3 \Rightarrow a = 3 \), \( b = 4 \)
Step 4: Verify altitude
Use: $h = \frac{a \cdot b}{c} $$= \frac{3 \cdot 4}{5} $$= \frac{12}{5} = 2.4 $
Step 5: Calculate Area
$ A = \frac{1}{2} \cdot a \cdot b $$= \frac{1}{2} \cdot 3 \cdot 4 $$= 6 \, \text{sq. meters} $
Step 6: Calculate Angles
$\alpha = \tan^{-1} \left( \frac{b}{a} \right) $$= \tan^{-1} \left( \frac{4}{3} \right) \approx 53.13^\circ$
$\beta = 90^\circ – \alpha = 36.87^\circ $
Frequently Asked Questions on Right Triangle Calculator
1. What does the Right Triangle Calculator do?
The Right Triangle Calculator helps you find any missing sides, angles, area, perimeter, or altitude of a right-angled triangle. You can input different combinations such as two sides, one side and one angle, area and side, or even perimeter and altitude to get accurate results.
2. What values can I enter?
You can enter any two known quantities among the triangle’s sides (perpendicular, base, or hypotenuse), angles, area, perimeter, or altitude. The calculator will determine all the remaining parts based on the given input.
3. Which formulas are used in this calculator?
The calculator uses several key geometric formulas:
- Pythagorean Theorem: \( c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} \)
- Area: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times a \times b \)
- Perimeter: \( P = a + b + c \)
- \( \alpha = \tan^{-1}\left(\frac{a}{b}\right) \)
- \( \beta = \tan^{-1}\left(\frac{b}{a}\right) \)
- Altitude Formula: \( h = \frac{a \times b}{c} \)
4. Can it calculate angles?
Yes. The calculator uses inverse trigonometric functions such as \(\tan^{-1}\), \(\sin^{-1}\), and \(\cos^{-1}\) to compute angles when the side values are provided.
5. Can I use it to verify triangle properties?
Absolutely. It’s an excellent tool for students and professionals to cross-check calculations, solve problems, or verify geometric constructions involving right-angled triangles.
6. What units does it support?
The calculator is unit-independent. You can input measurements in any unit (e.g., meters, feet, inches) as long as all values use the same unit. The output will also be in the same unit, and area in square units.
7. Is the calculator accurate?
Yes, it provides highly accurate results based on precise mathematical formulas. It also shows step-by-step solutions for better understanding.
8. Can I use this on mobile devices?
Yes, the Right Triangle Calculator is responsive and works smoothly on all devices—phones, tablets, and desktops—without the need to download any app.
9. Is it only for right-angled triangles?
Yes, this calculator is specifically designed for right triangles. For other triangle types, you should use a general triangle calculator.
10. Is it helpful for real-world use?
Definitely. This tool is used in various fields including construction, surveying, architecture, trigonometry, and academic purposes.
Final Thoughts: The Right Triangle Calculator helps to calculate any unknown value in a right-angled triangle—be it the perpendicular (a), base (B), hypotenuse (C), area (A), perimeter (P), angle α (Alpha), angle β (Beta), or altitude (H). By simply providing any two known values, the calculator intelligently applies geometric and trigonometric formulas to solve for the rest. It supports multiple units for length—meters (m), centimeters (cm), millimeters (mm), yards (yd), feet (ft), and inches (in)—as well as angle units in both degrees and radians. Whether you’re a student, teacher, engineer, or anyone working with triangles, this tool ensures fast, accurate, and unit-flexible results.
My Request to All: If you enjoy using my Right Triangle Calculator and my website, please consider sharing the link to this page or the website with your friends. Additionally, if you have any requests, complaints, suggestions, or feedback, feel free to reach out via our WhatsApp channel or Telegram group.
Telegram Link – Join Our Telegram Channel
YouTube Link – Subscribe to Our YouTube Channel
For more tools, please visit our homepage at CalculationClub – Free Online Calculators
For additional tools in Hindi, you can visit MeterToFeet