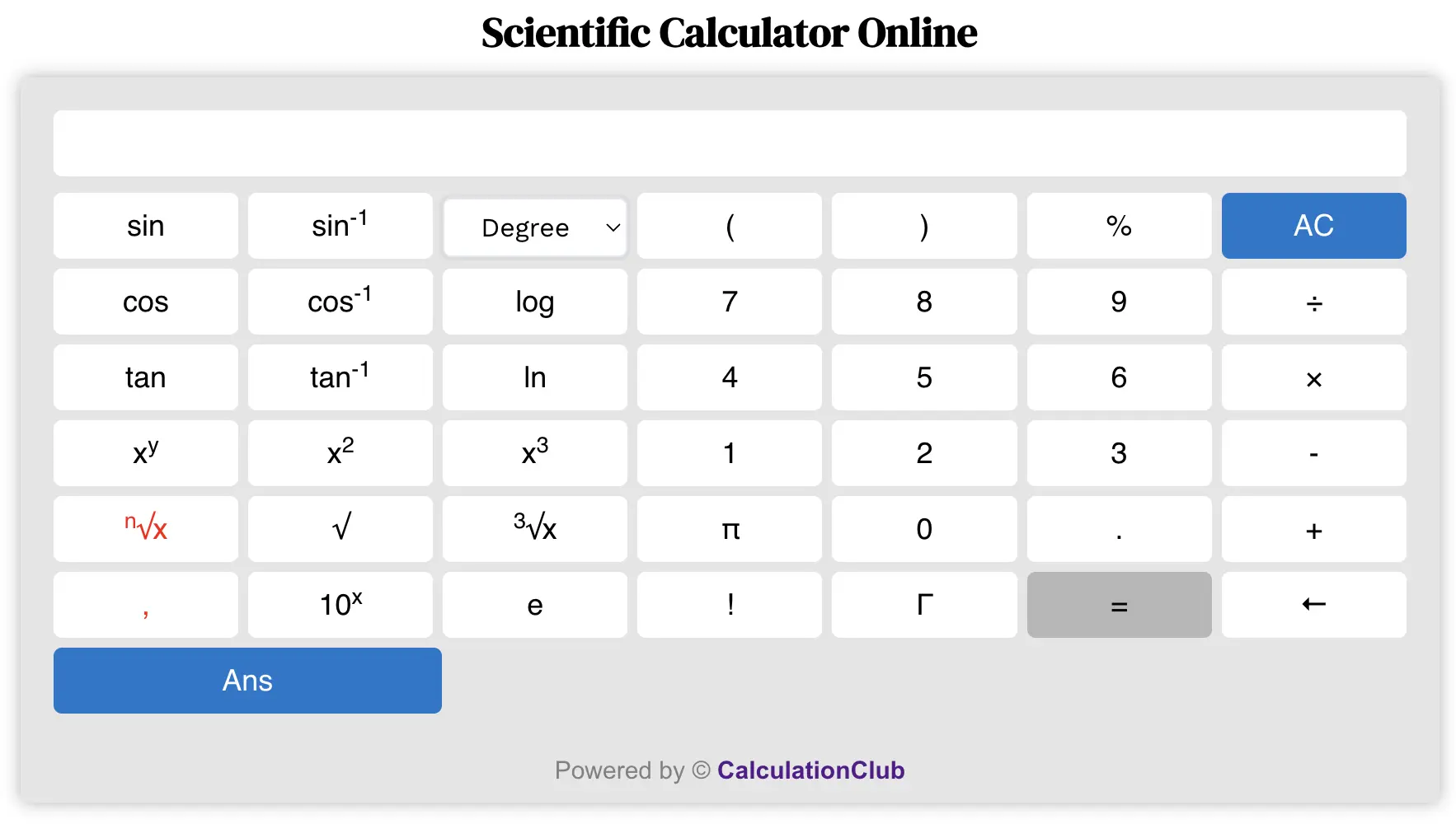
Scientific Calculator Online
Welcome to our Scientific Calculator Online – a powerful and user-friendly tool for solving both basic and complex mathematical problems. Whether you’re calculating simple arithmetic, trigonometric equations, logarithms, or using constants like π and Euler’s number, this tool provides everything you need – instantly and accurately.
It includes support for advanced functions such as factorial (!), gamma (Γ), square roots, powers, percentage, and more. With a clean interface and real-time output, you can solve math problems effortlessly on both desktop and mobile devices.
Features of the Scientific Calculator Online:
Scientific Calculator Online is more than just a digital number cruncher — it’s a full-featured math engine built for everything from everyday calculations to complex scientific and engineering problems.
💡 Whether you’re a student, teacher, engineer, or just a math enthusiast, this tool can handle it all — from basic arithmetic to advanced trigonometric and logarithmic operations. Below is a comprehensive guide to the powerful functions this tool offers:
➕ Basic Arithmetic Operations
Start with the fundamentals. This calculator performs all the standard operations:
- Addition (+): Add numbers quickly and accurately.
- Subtraction (−): Subtract one value from another with ease.
- Multiplication (×): Multiply large or small numbers instantly.
- Division (÷): Divide numbers with high precision.
📐 Trigonometric Functions (In Degrees or Radians)
- Sine (sin): Calculate the sine of an angle in degrees or radians.
- Cosine (cos): Determine the cosine of any angle with precision.
- Tangent (tan): Find the tangent of an angle in your selected unit.
- Arcsine (sin−1 or asin): Get the angle whose sine is a given value (range: −π/2 to π/2).
- Arccosine (cos−1 or acos): Get the angle with a known cosine (range: 0 to π).
- Arctangent (tan−1 or atan): Determine the angle from a given tangent (range: −π/2 to π/2).
✔️ Tip: Switch between degrees and radians with the calculator’s mode option for accurate results.
📈 Exponential & Logarithmic Functions
Perfect for algebra, calculus, and data science calculations:
- Exponentiation (xy): Raise any base to a power.
- Square (x2): Instantly square numbers.
- Cube (x3): Quickly compute cube values.
- Square Root (√x): Find the square root of any number.
- Cube Root (∛x): Calculate cube roots easily.
- nth Root (√nx): Solve any root-based expression.
- Natural Logarithm (ln): Log to base e (Euler’s number ≈ 2.71828).
- Common Logarithm (log): Logarithm to base 10, often used in scientific notation.
🎯 Other Advanced Mathematical Functions
- Percentage (%): Calculate percentages instantly and accurately.
- π (Pi): The constant π ≈ 3.14159, used in geometry and trigonometry.
- e (Euler’s Number): The base of natural logarithms (≈ 2.71828).
- Factorial (!): Useful for permutations, combinations, and statistics (e.g., 5! = 120).
- Gamma (Γ): Extends the factorial to non-integer values. Γ(n) = (n-1)!
- 10x: Calculates powers of 10 — vital in exponential growth and scientific notation.
🛠️ Additional Calculator Controls
The Scientific Calculator Online isn’t just powerful — it’s user-friendly too. Here are some utility buttons for better control:
- 🧹 Clear History: Double-click the AC button to wipe all past calculations.
- 🔁 AC (All Clear): Reset everything with a single tap.
- ⬅️ Backspace (←): Delete one character or digit if you make an error while typing.
- = Equals: Get your final result by pressing the equals button — simple and instant.
How to Use Our Scientific Calculator Online?
| Constants (π, e) | |
| Pi (π) and Euler’s Number (e): The buttons labeled “π” and “e” represent the mathematical constants pi (π) and Euler’s number (e), respectively. You can use them in calculations just like any other number. | |
| Addition (+) | |
To add two numbers, follow these steps:
| Example: 5+6=11 |
To add two numbers, one of which is negative, you can follow these steps:
| Example 1: Adding -5 and 6 Here’s how you can do it:
Example 2: Adding 5 and -6 Here’s how you can do it:
|
If you want to add two functions such as sin, cos, tan, sin-1, cos-1, tan-1, log, ln, π, e, etc., you can follow these steps:
| Example: sin(30) + log(10) = 1.5 Note: It is important to ensure that you close any brackets where necessary, as failing to do so may result in a different answer. Example: Let’s consider the expression sin(30+log(10). Breaking down the steps:
|
⇒ It is important to ensure that you close brackets where necessary, as failing to do so may result in a different answer. ⇒ As demonstrated in this example, the calculator automatically applies the closed bracket to the expression. However, it is still essential to be mindful of closing brackets when working with complex calculations to ensure accurate results. | |
| Subtraction (-) | |
| To subtract two numbers or functions, you can follow the same steps as an addition but with a slight change in the sign. | Example: 5 – 6 = -1 Example: 5 – (-6) = 11 Example: (-5) – 6 = -11 sin(30) – log(10) = -0.5 log(10) – sin(30)= 0.5 |
| Multiplication (×) | |
| To multiply two numbers or functions, you can follow the same steps as addition, but with a sign change. | Example: 5 × 6 = 30 Example: 5 × (-6) = -30 Example: (-5) × 6 = -30 sin(30) × log(10) = 0.5 × 1= 0.5 log(10) × (-sin(30))= 1×(-0.5) = 0.5 |
| Division (÷) | |
| To divide two numbers or functions, you can follow similar steps as mentioned for addition and multiplication, but with a sign change | Example: 30 ÷ 6 = 5 Example: 30 ÷ (-6) = -5 Example: (-30) ÷ 6 = -5 log(10) ÷ (-sin(30))= 1÷(-0.5) = -2 |
| Percentage (%) | |
To calculate a percentage of a number, follow these steps:
| Example: Finding 20% of 80
The calculator will display “20% × 80” (the multiplication symbol is automatically applied) indicating that 20% of 80 is 16. |
| Trigonometric Functions (sin, cos, tan) | |
To use the trigonometric functions on the online calculator, follow these simplified steps:
By following these simplified steps, you can easily use the trigonometric functions on the online calculator to calculate values based on the entered angles in both degrees and radians. | Example: sin(30) where angle in degree.
Example: sin(30) where angle in radian.
Example: sin(X). where X is the group of all functions present on the calculator. |
| In History Field sinD(30) = 0.5, where D stands for the selected mode which is that degree. sinR(30) = -0.9880316241, where R stands for the selected mode which is that Radian. | |
| Trigonometric Functions (sin-1, cos-1, tan-1) | |
To use the trigonometric functions on the online calculator, follow these simplified steps:
By following these simplified steps, you can easily use the trigonometric functions on the online calculator to calculate angles in both degrees and radians of different values. | Example: sin-1(0.5), we want to answer in degree.
Note:
|
| Logarithmic Functions (log, ln) | |
Logarithm (log): Use the “log” button to calculate the logarithm of a number. For example, to find the logarithm of 100, click the “log” button followed by the button labeled “100”. Similarly, you can use the “ln” button to calculate the natural logarithm (base e) of a number. Just follow the same steps as above, but use the “ln” button instead of “log”. | Example: log(100)
|
| Exponents | |
The online calculator offers functions for exponentiation, enabling you to perform calculations involving powers. Here’s a guide on how to use these operations: Exponentiation (^): To raise a number to a power, follow these steps:
Similarly These two buttons, “x²” and “x³,” on the online calculator function to calculate the square and cube of a number, respectively. By following these steps, you can easily perform exponentiation calculations using the online calculator. | Example: Calculating 2 raised to the power of 3
Result: The calculator will display the value of 2 raised to the power of 3, which is 8. Example: Calculating 2 raised to the power of -3.
Result: The calculator will display the value of 2 raised to the power of -3, which is 0.125. |
| Root | |
Square Root (√)
| Example: √25
Result: The calculator will display “5,” indicating the square root of 25 is 5. Similarly: [ √(X) ], where x is a group of functions. |
Cubic Root (√)
| Example: √25
Result: The calculator will display “5,” indicating the cubic root of 125 is 5. Similarly: [ √(X) ], where x is a group of functions or negative number. |
nth Root (n√x) To calculate the nth Root of a number, use the [ n√x ] button. There are two ways to use it. Method. 1 (If n is not a group of functions) If n= Real Numbers (positive integers, negative integers, fractions, and decimals, but excluding imaginary numbers.) and X= Any number or Group of Functions.
| Example.1: If we want a cubic root of 8. ( n=3 and x= 8)
Result: The calculator will display “2,” indicating the cubic root of 8 is 2. Example.2: If we want a cubic root of -8. ( n=3 and x= -8)
Result: The calculator will display “-2,” indicating the cubic root of -8 is 2. Example.2: If (n=-3 and x= 8)
Result: The calculator will display “0.5”. Similarly: [ n√(X) ], where x is a group of functions or negative number. |
If n= Any number or Group of Functions. and X= Any number or Group of Functions.
| Example:
|
| Factorials (!) | |
Online calculators provided by CalculationClub.com offer functionality to calculate factorials and the gamma function. Here’s how you can utilize these features: Factorial (!): To calculate the factorial of a number, follow these steps:
| Example: Calculating the factorial of 5
Result: The calculator will display “120,” which is the factorial of 5. Similarly: [ factorial(X) ], where x is a group of functions. |
| Gamma (Γ) | |
Gamma (Γ) Function: To calculate the gamma function of a number, follow these steps:
| Example: Calculating the gamma of 5
Result: The calculator will display “24,” which is the gamma of 5. Similarly: [ gamma(X) ], where x is a group of functions. |
| Using Parentheses ” (, ) “ | |
| The online calculator allows you to use parentheses to group operations. Parentheses are a powerful tool in mathematical calculations as they allow you to group operations. | |
| Memory Functions (Ans) | |
| Memory Functions: The “Ans” button represents the previous answer, which can be used in subsequent calculations. Click the “Ans” button to recall the previous result. | |
Key Features of the Scientific Calculator Online
- ✔️ All-in-One Calculator: From basic arithmetic to scientific operations – all functions in one tool.
- ✔️ Real-Time Results: Get instant feedback as you enter equations.
- ✔️ Mobile-Friendly: Fully responsive design for use on phones, tablets, and desktops.
- ✔️ Constants & Symbols: Includes Pi (π), e, factorial (!), and more.
- ✔️ Clean Interface: Intuitive layout with labeled buttons and display area.
Why Use Our Scientific Calculator Online?
- ✅ 100% Free to Use – No signup or payment required.
- ✅ Accurate & Reliable – Precision functions for all your math needs.
- ✅ Works on All Devices – Use it seamlessly on mobile, tablet, or desktop.
- ✅ No Data Stored – Your inputs remain private and are not saved.
Popular Uses for Scientific Calculator Online
- 📌 Solve algebraic and trigonometric equations
- 📌 Calculate logarithms, powers, and roots
- 📌 Evaluate factorials or use constants like π and e
- 📌 Perform quick scientific computations in school or work
FAQs – Scientific Calculator Online
1. What is a Scientific Calculator Online?
It’s an advanced web-based calculator used for performing basic to complex math calculations like trigonometry, exponentials, and logarithms.
2. Can I calculate in both degrees and radians?
Yes! You can choose between degrees and radians while using trigonometric functions.
3. Does this calculator support constants like Pi and e?
Absolutely. You can use π (Pi), e (Euler’s number), and more directly from the interface.
4. Is this tool mobile-friendly?
Yes, it’s fully responsive and works on any device – phone, tablet, or desktop.
5. Is my data saved anywhere?
No, all your calculations are done client-side. We do not store or track any input.
Conclusion: Our free Scientific Calculator Online is the perfect tool for students, teachers, engineers, or anyone needing quick and reliable mathematical solutions.
My Request to All: If you find this tool useful, please share it with your friends, students, or team. Explore more amazing tools at CalculationClub.
For Hindi tools, visit MeterToFeet
For educational notes, visit Esenotes
Your Feedback Matters: Have suggestions? Contact us via WhatsApp or Telegram – we love improving based on your input!
Telegram Link – Join Our Telegram Channel
YouTube Link – Subscribe to Our YouTube Channel