Scientific Calculator Online
Scientific Calculator Online is an advanced tool for calculating everything from basic math to advanced functions like trigonometry, exponents, and logarithms. It even has constants like π and Euler’s number, along with factorial and gamma functions, among others.
Scientific Calculator Online
- This “Scientific Calculator Online” from CalculationClub helps simplify your calculations effortlessly.
- You can easily perform various mathematical operations, from basic arithmetic to advanced functions like trigonometry, logarithms, exponents, roots, factorials, and even gamma calculations.
- It’s important to understand all its functions to use our calculator effectively. Scroll below to learn how to use: the Scientific Calculator Online.
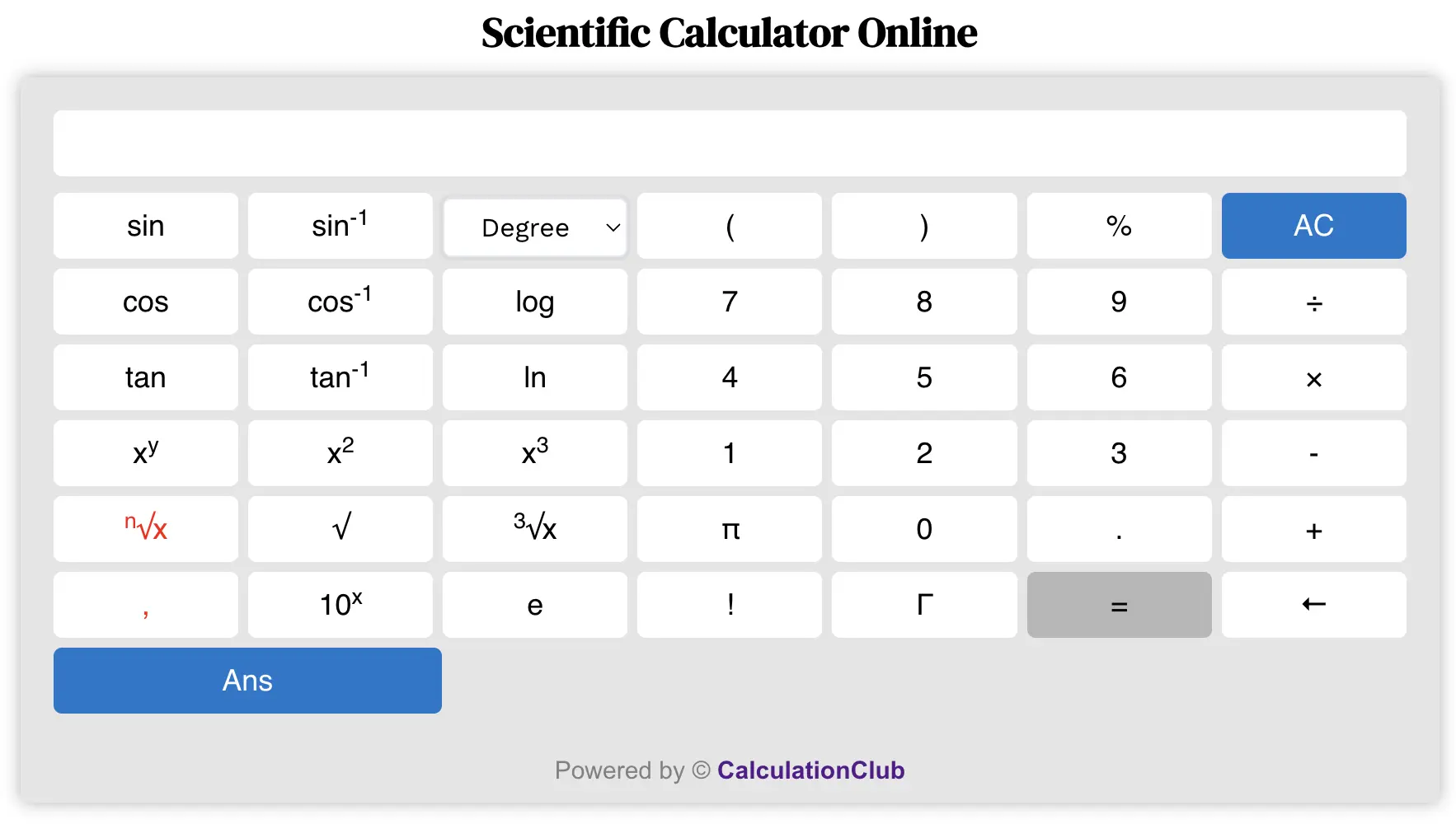
What Are the Functions of the Scientific Calculator Online?
Calculators are powerful tools that help us perform various mathematical calculations quickly and accurately. Whether it’s for simple arithmetic or complex scientific calculations, calculators provide a wide range of functions to meet our mathematical needs. In this blog post, we will explore the functions available on a Scientific Calculator Online and understand how they can be used.
Basic Arithmetic Operations
Let’s start with the basic arithmetic operations that every calculator offers:
- Addition (+)
- Subtraction (-)
- Multiplication (×)
- Division (÷)
Trigonometric Functions
- Sine (sin): This function calculates the sine of an angle. The user can input an angle in degrees or radians, and the calculator will return the corresponding sine value.
- Cosine (cos): This function calculates the cosine of an angle. Similar to the sine function, the user can input an angle in degrees or radians, and the calculator will return the corresponding cosine value.
- Tangent (tan): This function calculates the tangent of an angle. Once again, the user can input an angle in degrees or radians, and the calculator will return the corresponding tangent value.
- Arcsine (sin-1 or asin): The arcsine function, denoted as sin-1 or asin, calculates the angle (in degrees or radians) whose sine equals a given value. The input of arcsin(x) must be within the range of -1 to 1. The output of arcsin(x) is always between -π/2 and π/2 in radians. In terms of domain and range, arcsin(x) has a domain of [-1, 1] and a range of [-π/2, π/2]. This function is commonly used to find an angle when the sine value is known.
- Arccosine (cos-1 or acos): The arccosine function, denoted as cos-1 or acos, calculates the angle (in degrees or radians) whose cosine equals a given value. The input of arccos(x) must be within the range of -1 to 1. The output of arccos(x) is always between 0 and π in radians. In terms of domain and range, arccos(x) has a domain of [-1, 1] and a range of [0, π]. This function is commonly used to find an angle when the cosine value is known.
- Arctangent (tan-1 or atan): The arctangent function, denoted as tan-1 or atan, calculates the angle (in degrees or radians) whose tangent equals a given value. The input of arctan(x) can take any real number as it has a range of (-∞, ∞). The output of arctan(x) is always between -π/2 and π/2 in radians or -90° and 90° in degrees.
These trigonometric functions can be calculated in degrees or radians, depending on the mode selected by the calculator.
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
Exponential and logarithmic functions are used in various mathematical and scientific calculations. Calculators often provide functions for these operations:
- Exponentiation (x^y)
- Square (x^2)
- Cube (x^3)
- Square Root (√x)
- Cube Root (3√x)
- nTh Root (n√x)
- Natural Logarithm (ln): The natural logarithm function calculates the logarithm of a number to the base “e,” where “e” is the mathematical constant approximately equal to 2.71828.
- Common Logarithm (log): The common logarithm function calculates the logarithm of a number to the base 10.
Other Functions
In addition to the basic arithmetic, trigonometric, exponential, and logarithmic functions, calculators often provide several other useful functions. Here are a few examples:
- Percentage (%): The percentage function calculates a percentage of a given number.
- Pi (π): The pi function represents the mathematical constant π, which is approximately equal to 3.14159. It is widely used in geometry and trigonometry.
- Euler’s Number (e): Euler’s number, denoted by the letter “e,” is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 2.71828. It is often used in exponential and logarithmic calculations.
- Factorial (!): The factorial function calculates the product of all positive integers up to a given number.
- Gamma (Γ): The gamma function is a mathematical extension of the factorial function. It calculates the value of factorial for non-integer numbers. The gamma function is denoted by the Greek letter Γ.
- 10x: The 10x function raises 10 to a given power, useful for calculations involving powers of 10.
Additional Buttons on the Calculator
In addition to the functions we discussed earlier, online calculators often include several other buttons that serve specific purposes. Let’s explore these buttons:
- Clear History: To clear the history, simply double-click the AC button. This action will clear the history, enabling you to begin anew with a fresh slate.
- AC (All Clear): The “AC” button performs an all-clear function. When pressed, it clears the display and any pending calculations, resetting the calculator to its initial state.
- Backspace (←): The backspace button, often represented by a left-pointing arrow (←), allows you to delete the last entered digit or character. It comes in handy when you make a mistake while entering a number or expression.
- Equals (=): The equals button (=) is used to perform the calculation and obtain the result. When pressed, it evaluates the entered expression and displays the calculated value on the screen.
How to Use Our Scientific Calculator Online?
| Constants (π, e) | |
| Pi (π) and Euler’s Number (e): The buttons labeled “π” and “e” represent the mathematical constants pi (π) and Euler’s number (e), respectively. You can use them in calculations just like any other number. | |
| Addition (+) | |
To add two numbers, follow these steps:
| Example: 5+6=11 |
To add two numbers, one of which is negative, you can follow these steps:
| Example 1: Adding -5 and 6 Here’s how you can do it:
Example 2: Adding 5 and -6 Here’s how you can do it:
|
If you want to add two functions such as sin, cos, tan, sin-1, cos-1, tan-1, log, ln, π, e, etc., you can follow these steps:
| Example: sin(30) + log(10) = 1.5 Note: It is important to ensure that you close any brackets where necessary, as failing to do so may result in a different answer. Example: Let’s consider the expression sin(30+log(10). Breaking down the steps:
|
⇒ It is important to ensure that you close brackets where necessary, as failing to do so may result in a different answer. ⇒ As demonstrated in this example, the calculator automatically applies the closed bracket to the expression. However, it is still essential to be mindful of closing brackets when working with complex calculations to ensure accurate results. | |
| Subtraction (-) | |
| To subtract two numbers or functions, you can follow the same steps as an addition but with a slight change in the sign. | Example: 5 – 6 = -1 Example: 5 – (-6) = 11 Example: (-5) – 6 = -11 sin(30) – log(10) = -0.5 log(10) – sin(30)= 0.5 |
| Multiplication (×) | |
| To multiply two numbers or functions, you can follow the same steps as addition, but with a sign change. | Example: 5 × 6 = 30 Example: 5 × (-6) = -30 Example: (-5) × 6 = -30 sin(30) × log(10) = 0.5 × 1= 0.5 log(10) × (-sin(30))= 1×(-0.5) = 0.5 |
| Division (÷) | |
| To divide two numbers or functions, you can follow similar steps as mentioned for addition and multiplication, but with a sign change | Example: 30 ÷ 6 = 5 Example: 30 ÷ (-6) = -5 Example: (-30) ÷ 6 = -5 log(10) ÷ (-sin(30))= 1÷(-0.5) = -2 |
| Percentage (%) | |
To calculate a percentage of a number, follow these steps:
| Example: Finding 20% of 80
The calculator will display “20% × 80” (the multiplication symbol is automatically applied) indicating that 20% of 80 is 16. |
| Trigonometric Functions (sin, cos, tan) | |
To use the trigonometric functions on the online calculator, follow these simplified steps:
By following these simplified steps, you can easily use the trigonometric functions on the online calculator to calculate values based on the entered angles in both degrees and radians. | Example: sin(30) where angle in degree.
Example: sin(30) where angle in radian.
Example: sin(X). where X is the group of all functions present on the calculator. |
| In History Field sinD(30) = 0.5, where D stands for the selected mode which is that degree. sinR(30) = -0.9880316241, where R stands for the selected mode which is that Radian. | |
| Trigonometric Functions (sin-1, cos-1, tan-1) | |
To use the trigonometric functions on the online calculator, follow these simplified steps:
By following these simplified steps, you can easily use the trigonometric functions on the online calculator to calculate angles in both degrees and radians of different values. | Example: sin-1(0.5), we want to answer in degree.
Note:
|
| Logarithmic Functions (log, ln) | |
Logarithm (log): Use the “log” button to calculate the logarithm of a number. For example, to find the logarithm of 100, click the “log” button followed by the button labeled “100”. Similarly, you can use the “ln” button to calculate the natural logarithm (base e) of a number. Just follow the same steps as above, but use the “ln” button instead of “log”. | Example: log(100)
|
| Exponents | |
The online calculator offers functions for exponentiation, enabling you to perform calculations involving powers. Here’s a guide on how to use these operations: Exponentiation (^): To raise a number to a power, follow these steps:
Similarly These two buttons, “x²” and “x³,” on the online calculator function to calculate the square and cube of a number, respectively. By following these steps, you can easily perform exponentiation calculations using the online calculator. | Example: Calculating 2 raised to the power of 3
Result: The calculator will display the value of 2 raised to the power of 3, which is 8. Example: Calculating 2 raised to the power of -3.
Result: The calculator will display the value of 2 raised to the power of -3, which is 0.125. |
| Root | |
Square Root (√)
| Example: √25
Result: The calculator will display “5,” indicating the square root of 25 is 5. Similarly: [ √(X) ], where x is a group of functions. |
Cubic Root (√)
| Example: √25
Result: The calculator will display “5,” indicating the cubic root of 125 is 5. Similarly: [ √(X) ], where x is a group of functions or negative number. |
nth Root (n√x) To calculate the nth Root of a number, use the [ n√x ] button. There are two ways to use it. Method. 1 (If n is not a group of functions) If n= Real Numbers (positive integers, negative integers, fractions, and decimals, but excluding imaginary numbers.) and X= Any number or Group of Functions.
| Example.1: If we want a cubic root of 8. ( n=3 and x= 8)
Result: The calculator will display “2,” indicating the cubic root of 8 is 2. Example.2: If we want a cubic root of -8. ( n=3 and x= -8)
Result: The calculator will display “-2,” indicating the cubic root of -8 is 2. Example.2: If (n=-3 and x= 8)
Result: The calculator will display “0.5”. Similarly: [ n√(X) ], where x is a group of functions or negative number. |
If n= Any number or Group of Functions. and X= Any number or Group of Functions.
| Example:
|
| Factorials (!) | |
Online calculators provided by CalculationClub.com offer functionality to calculate factorials and the gamma function. Here’s how you can utilize these features: Factorial (!): To calculate the factorial of a number, follow these steps:
| Example: Calculating the factorial of 5
Result: The calculator will display “120,” which is the factorial of 5. Similarly: [ factorial(X) ], where x is a group of functions. |
| Gamma (Γ) | |
Gamma (Γ) Function: To calculate the gamma function of a number, follow these steps:
| Example: Calculating the gamma of 5
Result: The calculator will display “24,” which is the gamma of 5. Similarly: [ gamma(X) ], where x is a group of functions. |
| Using Parentheses ” (, ) “ | |
| The online calculator allows you to use parentheses to group operations. Parentheses are a powerful tool in mathematical calculations as they allow you to group operations. | |
| Memory Functions (Ans) | |
| Memory Functions: The “Ans” button represents the previous answer, which can be used in subsequent calculations. Click the “Ans” button to recall the previous result. | |
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Scientific Calculator Online provides a versatile tool for performing calculations quickly and accurately. By following the step-by-step examples provided, you can easily input numbers and symbols, utilize operator buttons, and perform a variety of mathematical operations. Whether you need to perform simple math calculations, calculate percentages, or determine present or future values, the Online Calculator can assist you in achieving accurate results. Take advantage of the calculator’s functionality to enhance your productivity and streamline your mathematical calculations.